|
Key Takeaways:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are common types of talk therapies used to treat various mental health issues.
- DBT is a branch of CBT and both therapies share similarities.
- CBT focuses on changing negative thinking patterns and behaviors.
- DBT focuses on acceptance, regulating intense emotions, and improving interpersonal relationships.
- CBT is best for conditions like anxiety and depression while DBT is more suited for people with borderline personality disorder.
|
There are many types of therapy used to treat mental health issues. Two of the most widely used therapeutic methods include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT). CBT and DBT belong to a class of treatments that fall under psychotherapy, more commonly recognized as talk therapy. This helps individuals solve problems, change behavior, and improve their overall well-being.
These two types of therapy have many things in common, but they also have significant differences. Here, we’ll discuss CBT vs DBT and how each type of therapy can help individuals in need.
What is CBT?
CBT or cognitive behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapeutic intervention that helps people recognize negative thinking patterns and how these impact their behaviors. With the help of a therapist, one can restructure their thoughts and behaviors in healthier ways.
While CBT is most often used to treat individuals with mental health conditions, this type of therapy is not exclusive to them. Others can also take advantage of CBT to improve their thoughts and behaviors that may be affected by problems in life, such as stress and other more specific circumstances. CBT can also be used by people of all ages.
Foundational Philosophy of CBT
The philosophical foundation of CBT is based on the premise that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are all connected. CBT operates on the principle that thoughts influence emotions and behaviors. By identifying and changing negative thought patterns with the help of CBT, we can improve our emotional responses and behaviors.
The emphasis on reasoning and rationale in CBT comes from its roots in stoic philosophy and the Socratic Method, which encourages critical thinking and draws out underlying assumptions. It helps individuals with conditions such as anxiety and depression see their issues from a more logical perspective.
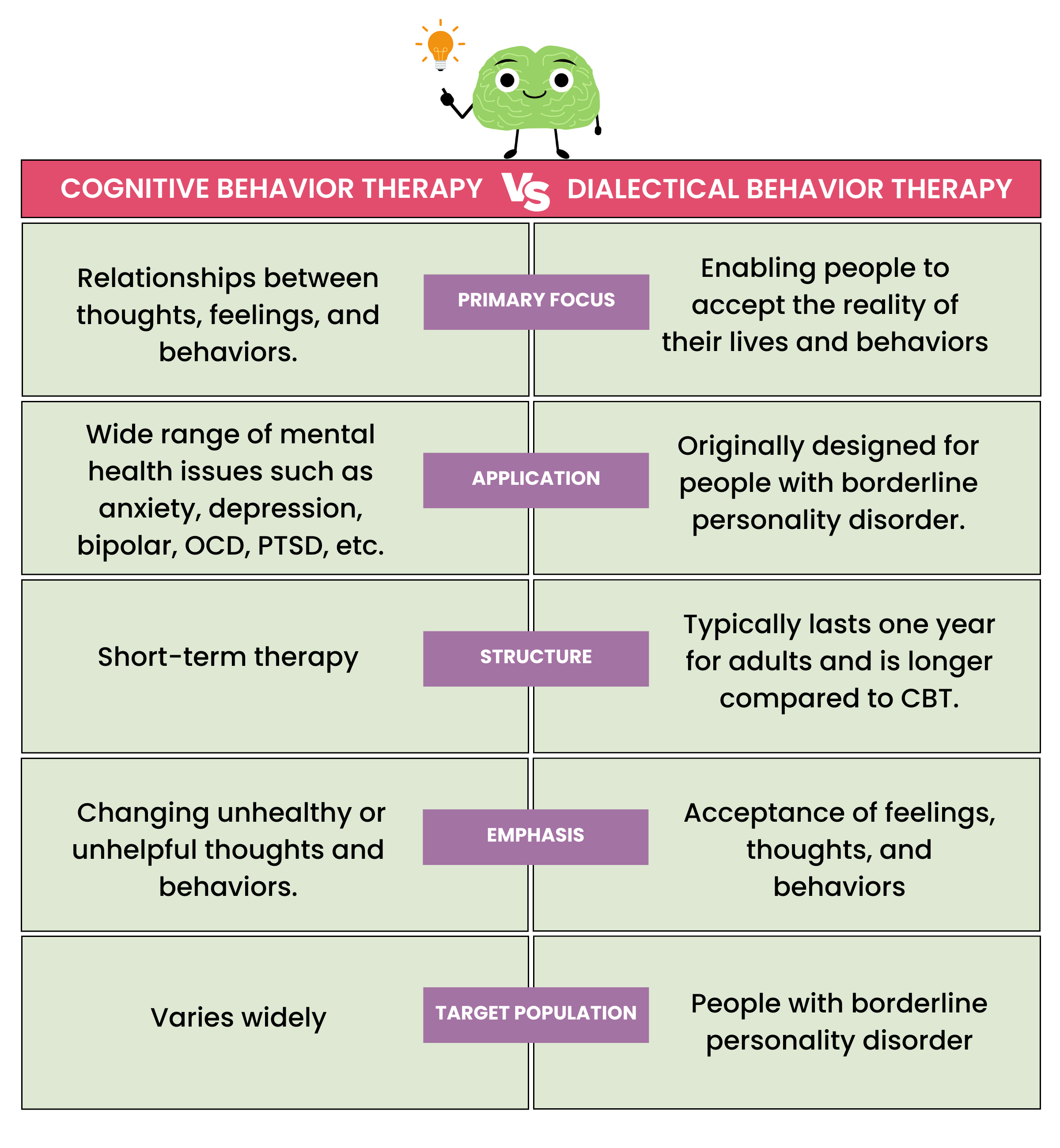
Primary Focus of CBT
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors and how they influence a person’s quality of life. It also centers on changing automatic negative thoughts that worsen our emotional difficulties. You learn how to identify, challenge, and replace faulty thoughts with more helpful and realistic ones.
Application of CBT
CBT can treat a wide range of issues. It is often the preferred type of therapy for many people for this reason. In general, CBT also requires fewer sessions compared to other types of therapy, so you can see results sooner.
When used as a tool to address emotional challenges, CBT can help you with the following:
- Manage symptoms of mental illness and prevent relapse of symptoms
- Treat mental illness if medications aren’t a good option
- Identify ways to manage emotions
- Learn techniques for coping with stressful life situations
- Better communication
- Conflict resolution
- Cope with grief or loss
- Manage chronic physical symptoms
- Cope with a medical illness
- Overcome emotional trauma related to abuse or violence
CBT can help the following mental health conditions improve:
CBT may be combined with other treatments, such as medications, to treat such conditions more effectively.
Structure of CBT
Cognitive behavioral therapy is structured as a short-term therapy. This ensures that individuals can achieve significant change within a defined time frame, typically lasting a few weeks to several months.
Emphasis of CBT
The main emphasis of CBT is changing unhealthy or unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. This type of therapy helps patients deal with negative and overwhelming problems in more constructive and positive ways to improve how they feel.
Target Population of CBT
The target population of cognitive behavioral therapy varies widely. This is because CBT can be used for a great number of mental health issues as mentioned above. Some individuals even use this therapy to help with chronic health conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia. Most importantly, CBT is for people who want to take an active role in their healing journey.
However, CBT may not be for people who have brain diseases, brain injuries, or other problems that affect thinking.
What is DBT?
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is another type of talking therapy that is a branch of CBT specially adapted for people who feel emotions very intensely. It involves more techniques in mindfulness and emotional regulation.
“Dialectical” means understanding that two opposing ideas can be true at the same time. For instance, DBT may encourage you to accept yourself and change your behavior all at once. This therapy teaches you that it is possible to achieve both.
DBT aims to help individuals understand and accept difficult feelings, learn skills to manage emotions, and make positive changes in life.
Foundational Philosophy of DBT
Dialectical philosophy is the philosophical foundation of DBT, which is based on the notion that opposites are interconnected and truth can emerge from conflicting ideas. This form of psychotherapy was created by Dr. Marsha M. Linehan for individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD).
DBT combines elements of Western cognitive-behavioral therapies with Eastern mindfulness practices. These techniques are found in Buddhist and Zen practices. This type of therapy emphasizes accepting things as they are rather than forcing change.
Primary Focus of DBT
DBT focuses on enabling people to accept the reality of their lives and behaviors while, at the same time, helping them learn how to change their lives, including their unhelpful behaviors. It does this through the DBT skills of mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. Validation in therapy as well as behavioral change are also important aspects of DBT.
Application of DBT
DBT was designed originally for individuals with BPD to help them cope with intense emotions, but it can also be used as an effective treatment for the following conditions:
- Bipolar disorder
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- Borderline personality disorder
- Major depressive disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Non-suicidal self-injury
- Suicidal behavior
- Substance use disorder
- Eating disorders
Structure of DBT
DBT is structured according to four modes of treatment: individual psychotherapy, skills training groups, therapist consultation team meetings (to prevent therapist burnout), and access to 24-hour per day telephone coaching from the therapist or skills group leader [*]. DBT typically lasts one year for adults and is longer compared to CBT.
Emphasis of DBT
DBT emphasizes the acceptance of feelings, thoughts, and behaviors while teaching patients the skills and techniques to change them for the better. Personal skills are taught in DBT as well as interpersonal competencies for relationships. DBT is based on CBT but places more emphasis on the social and emotional aspects of living.
Target Population of DBT
DBT is designed specifically for people with borderline personality disorder but can also be for people who have difficulty controlling their emotions. This type of treatment can be used for other conditions, as mentioned above.
CBT vs. DBT: Which Therapy is Best for You?
Though these therapies have similar outcome goals, there are key differences between CBT and DBT. CBT is more of a short-term treatment while DBT typically requires a one-year commitment. While DBT focuses on changing negative thoughts and emotions, DBT encourages accepting negative emotions, feeling them, and then letting them go.
People with depression and anxiety have found plenty of success with CBT [*], while individuals with borderline personality disorder and chronic suicidal thoughts may find DBT more helpful [*]. Remember that people may have more than one diagnosis and that elements from CBT or DBT can be used to manage symptoms.
Can You Combine CBT and DBT?
Yes, you can combine CBT and DBT depending on the needs of the client.
It is common for therapists to integrate aspects of both CBT and DBT to help their clients meet their treatment goals. Some clients may also receive CBT from one therapist and participate in DBT group therapy with another mental health professional.
The Bottom Line
CBT and DBT therapy methods are both helpful in treating individuals experiencing various mental illnesses. Deciding which one is best for you will depend on your specific symptoms and what type of treatment you are most comfortable with. Learning as much as you can about these methods is an important stepping stone to your well-being.
Remember, consulting a mental health professional is the best way to determine the best type of therapy for your needs.
For more therapeutic resources, check out our CBT worksheets and DBT worksheets. Our worksheets provide visual and written engagement to support different modalities of learning, which can enhance traditional talk or play therapy.
References:
- Frazier S & Vela J. Dialectical behavior therapy for the treatment of anger and aggressive behavior: A review. March-April 2014.
- Bogucki O, Craner J, Berg S et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for depressive disorders: Outcomes from a multi-state, multi-site primary care practice. November 2021.
- DeCou C, Comtois K, Landes S. Dialectical Behavior Therapy Is Effective for the Treatment of Suicidal Behavior: A Meta-Analysis. January 2019.






















































