The Power Of Movement For The ADHD Brain
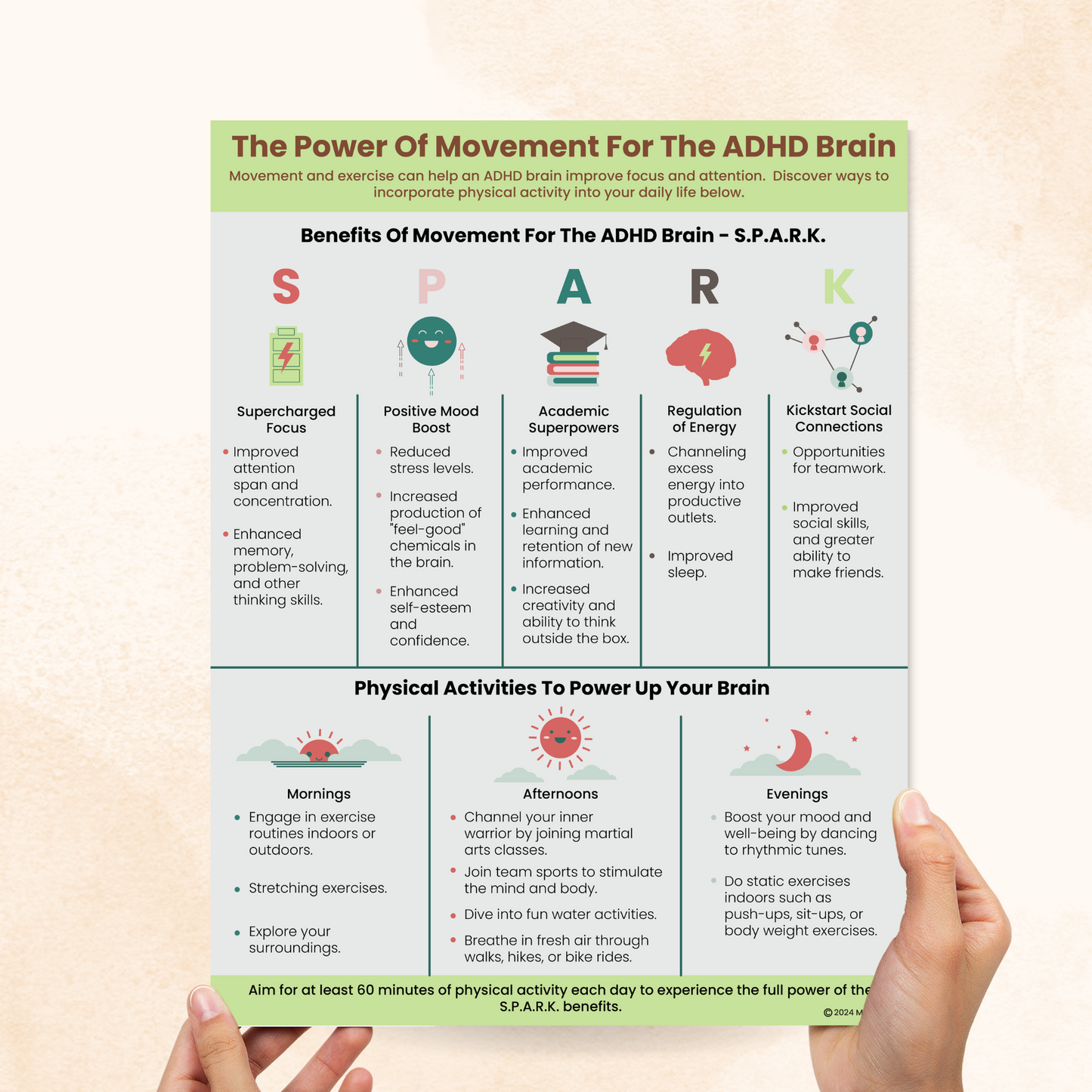
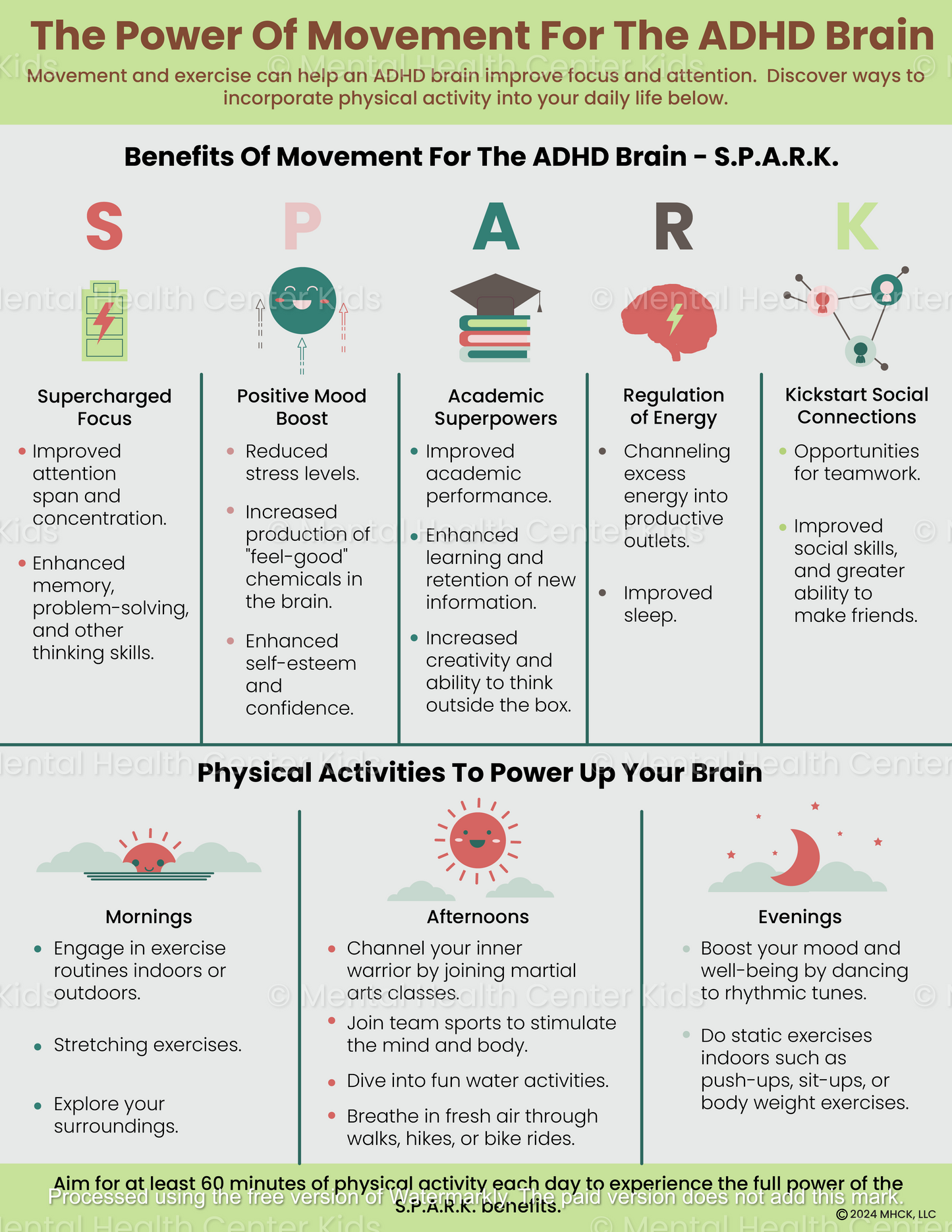

Physical movement encompasses any bodily action, such as walking, jumping, or running. With constant activity, the brain stays alert and focused, which enhances an individual’s ability to pay attention. This is particularly important for clients with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
The Power Of Movement For The ADHD Brain highlights the benefits of physical activity for individuals with ADHD, even simple ones like stretching and dancing. A list of suggested physical activities to try in the morning, afternoon, or evening is also included in the second part of the handout.
Kids and teens using this handout can benefit from increased levels of beneficial brain chemicals, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which can enhance focus, attention, mood, and energy levels—similar to the effects of ADHD medication. Parents and teachers can support these efforts by creating a simple weekly plan that incorporates the activities suggested in the handout.
Find this handout in our ADHD Handouts Bundle along with 28 additional pages of visually appealing resources to support kids and teens with ADHD.
*This item is an instant digital download. A link to download your files will be emailed to you once payment is confirmed.
Want more resources like this? Check out our full catalog of ADHD worksheets and handouts.
References:
- Benzing, V., Chang, Y., & Schmidt, M. (2018). Acute physical activity enhances executive functions in children with ADHD. Scientific Reports, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30067-8
- Harvey, W. J. (2006). Fundamental movement skills and associated physical activity experiences of children with ADHD. McGill University.
- Xie, Y., Gao, X., Song, Y., Zhu, X., Chen, M., Yang, L., & Ren, Y. (2021). Effectiveness of physical activity intervention on ADHD symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.706625
- Ziereis, S., & Jansen, P. (2015). Effects of physical activity on executive function and motor performance in children with ADHD. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 38, 181-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.12.005
- Instant digital download
- File: PDF
- Size: 8.5" x 11"




